The Code That Runs the Future: Understanding How DeFi Works Starts with Smart Contracts

Welcome back to DefiAnalyticsHub.com, your home for navigating the world of decentralized finance. Our last post gave you a high-level overview of DeFi, but to truly understand this financial revolution, you need to go one layer deeper.
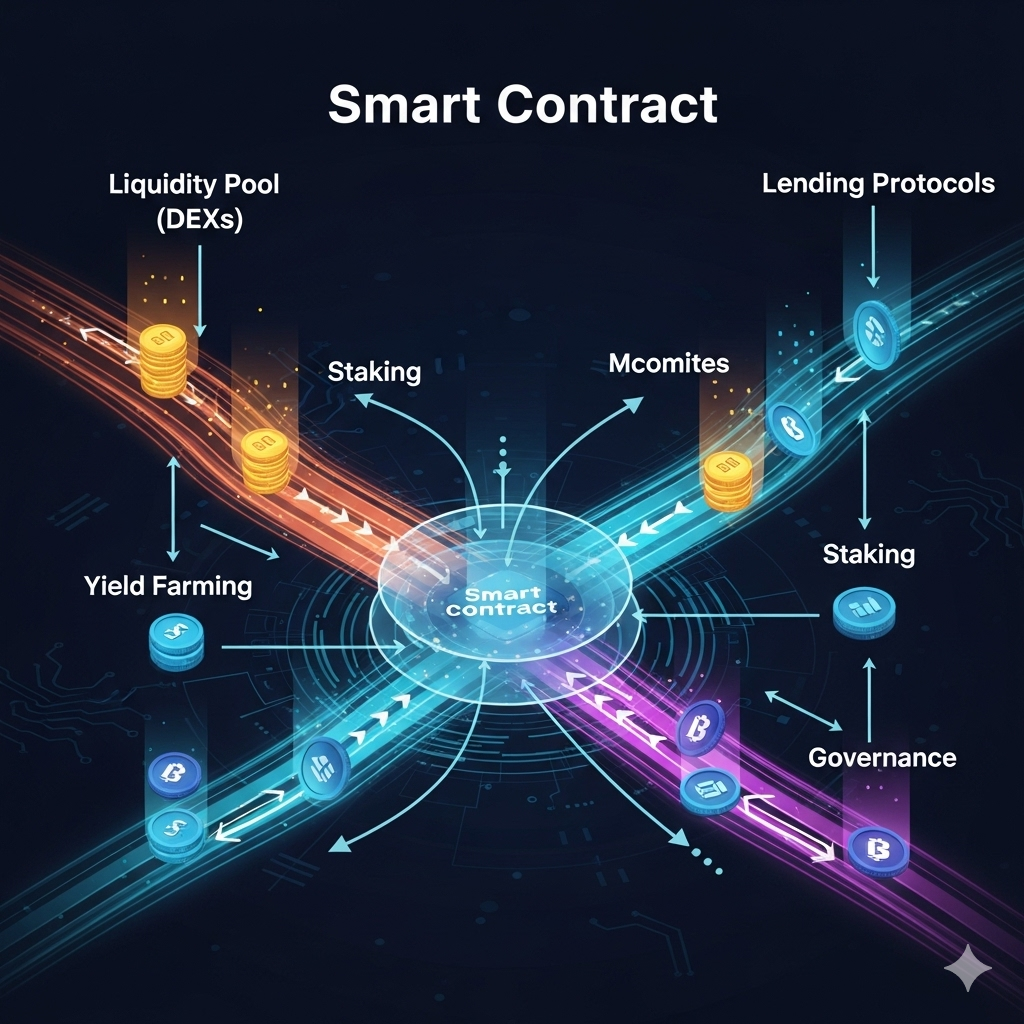
The single most important concept in all of DeFi is the smart contract. Forget banks, brokers, or legal agreements on paper. In DeFi, the rules are not written in a legal document, but in code. Smart contracts are the engine, the law, and the infrastructure that make decentralized finance possible. This post will break down what they are, how they work, and why they are the key to a new, transparent financial system.
What is a Smart Contract?
A Vending Machine for Money vending machine for money: think of a smart contract as a digital vending machine. You don’t need to trust a person to give you the right snack or change. You simply put in the correct amount of money, select your item, and the machine automatically dispenses your order. The rules (“If I receive $1.50 and button ‘B5’ is pressed, then dispense a bag of chips”) are programmed into the machine and execute without any human intervention.
A smart contract is exactly like that, but for financial transactions. It’s a self-executing agreement with the terms of the deal written directly into lines of code. This code is stored on a decentralized blockchain network, like Ethereum. Once deployed, it runs automatically and transparently, with no need for a central authority or intermediary.
How Smart Contracts Power DeFi: Replacing the Middleman
In traditional finance, every service—lending, borrowing, trading—requires an intermediary. A bank holds your savings, a broker executes your trades, and a lawyer drafts your loan agreements.
DeFi uses smart contracts to perform all these functions automatically. Instead of a bank holding your money, a smart contract holds the funds in a “liquidity pool.” Instead of a broker matching buyers and sellers, a smart contract uses an algorithm to facilitate trades. This is the essence of why DeFi is considered trustless and permissionless. You don’t need to trust a third party because the code, which is transparent and verifiable by anyone, handles the entire process.
This is the very foundation of how DeFi works. It’s all about automating a “if this, then that” logic for financial transactions, executed by a decentralized network.
Smart Contracts in Action: From Lending to Trading
To truly grasp the power of smart contracts, let’s look at how they function in some common DeFi applications.
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): When you swap one crypto for another on a DEX like Uniswap, you’re not trading with a specific person. Instead, you’re interacting with a smart contract that manages a liquidity pool. The contract uses an Automated Market Maker (AMM) algorithm to calculate the exchange rate and execute the trade instantly and automatically. This is a perfect example of DeFi crypto trading powered by code alone.
- Lending Protocols: On platforms like Aave or Compound, smart contracts manage the entire borrowing and lending process. A user deposits assets into a smart contract to earn interest. Another user can then borrow from that same contract by putting up collateral. The smart contract automatically handles the interest rates, collateral management, and liquidations if a borrower’s collateral falls below a certain threshold—all without any human intervention.
Benefits and Risks of the Code
The reliance on smart contracts brings significant advantages to the decentralized finance in crypto space, but also introduces unique risks.
Benefits:
- Automation and Efficiency: Smart contracts execute instantly, 24/7, without the delays of traditional banking.
- Transparency: All smart contract code and every transaction it performs are visible on the blockchain, creating an auditable, public record. This is a core part of DeFi analytics.
- Trustlessness: You don’t need to trust a person or company; you only need to trust the code.
Risks:
- Code Vulnerabilities: If a smart contract contains a bug, it can be exploited by malicious actors, leading to significant financial losses.
- Immutable Code: Once a contract is deployed, it’s very difficult to change. A flaw in the original design can be permanent unless a workaround is built.
Looking Ahead: The Future is Programmable
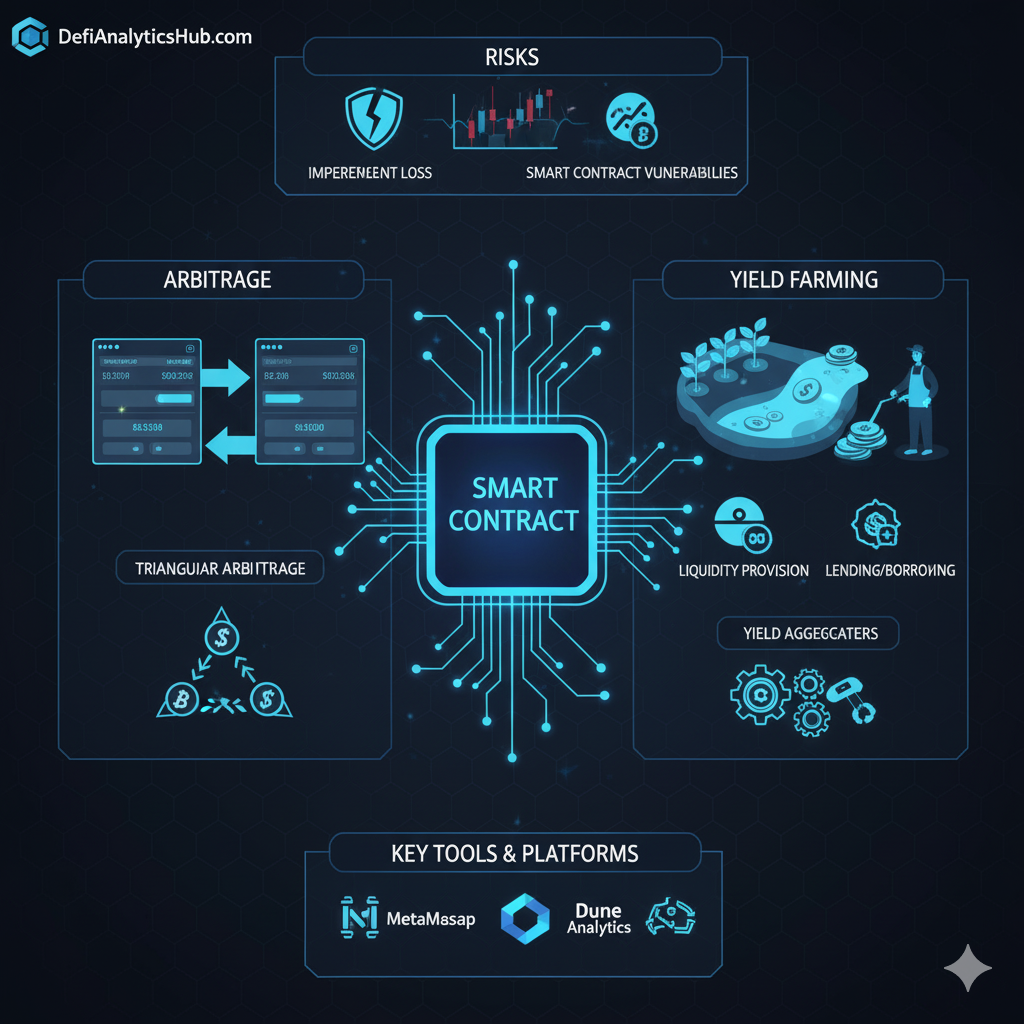
Smart contracts are the foundational layer of DeFi, a space where innovation moves at breakneck speed. From complex tokenomics models to sophisticated yield farming strategies, every new development in understanding DeFi is built on top of this powerful, programmable infrastructure. As more developers and projects enter the space, the “money legos” of DeFi will continue to stack, creating ever more complex and useful financial applications.
For our advanced readers, the next time you analyze a protocol’s DeFi analytics, remember that you are not just looking at numbers; you are looking at the output of millions of lines of code working together in a truly decentralized manner. This is just the beginning of what’s possible with programmable money.


 English
English